Индикаторы технического анализа на Форекс
Мастерство трейдинга на Форекс: научись читать рынок с помощью индикаторов технического анализа и принимай верные решения! Узнай секреты успешной торговли – риски минимальны, прибыль максимальна!
Торговля на валютном рынке Форекс – это увлекательное, но и рискованное занятие. Успех в этой сфере во многом зависит от правильного анализа рынка и принятия обоснованных решений. Одним из ключевых инструментов, помогающих трейдерам в этом непростом деле, являются индикаторы технического анализа. Они предоставляют визуальное представление о динамике цен и позволяют прогнозировать будущие движения рынка; На странице https://example.com вы найдете множество полезной информации о различных индикаторах. Правильное использование индикаторов значительно увеличивает шансы на прибыльную торговлю, но требует глубокого понимания их принципов работы и особенностей применения.
Выбор подходящего индикатора
Рынок Форекс предлагает огромное количество различных индикаторов, каждый из которых имеет свои преимущества и недостатки. Выбор оптимального индикатора зависит от индивидуальной торговой стратегии, временного интервала и уровня риска, который трейдер готов принять. Некоторые индикаторы лучше подходят для краткосрочной торговли (скальпинг), другие – для долгосрочных инвестиций (свинговая торговля). Важно понимать, что ни один индикатор не может гарантировать 100% прибыли, и их следует использовать в комплексе с другими методами анализа.
Популярные индикаторы для Форекс
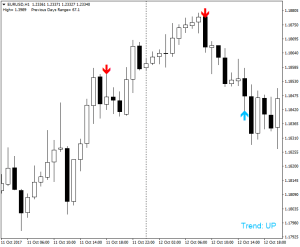
- Скользящие средние (Moving Average)⁚ Один из самых распространенных индикаторов, который сглаживает колебания цен и помогает определить тренд. Существуют различные типы скользящих средних, например, простые, экспоненциальные и взвешенные.
- MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence)⁚ Индикатор, основанный на разнице между двумя скользящими средними. Он помогает определить моменты смены тренда и возможные точки разворота.
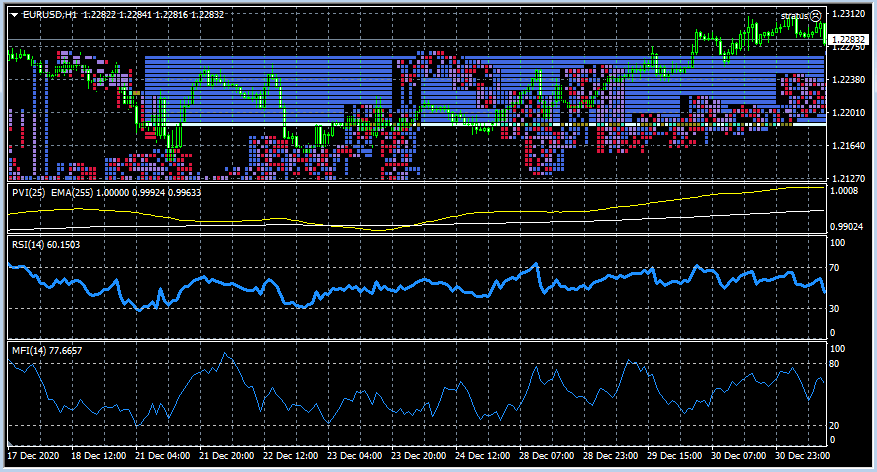
- RSI (Relative Strength Index)⁚ Отображает силу тренда и помогает определить перекупленность или перепроданность рынка. Часто используется для определения потенциальных точек входа и выхода из сделки.
- Стохастик (Stochastic Oscillator)⁚ Индикатор, измеряющий импульс цены. Он помогает определить моменты перекупленности и перепроданности, а также возможные точки разворота.
- Bollinger Bands⁚ Индикатор, представляющий собой канал, образованный скользящей средней и двумя стандартными отклонениями от неё. Помогает определить волатильность рынка и потенциальные точки разворота.
Использование индикаторов в комплексе
Для повышения точности прогнозов рекомендуется использовать несколько индикаторов одновременно. Комбинация индикаторов позволяет получить более полную картину состояния рынка и подтвердить сигналы, генерируемые отдельными индикаторами. Например, сочетание скользящих средних и MACD может помочь определить начало и конец тренда, а RSI и Стохастик – подтвердить сигналы о перекупленности или перепроданности.
Сигналы индикаторов и управление рисками
Важно помнить, что сигналы, генерируемые индикаторами, не являются абсолютной истиной. Они лишь помогают в принятии торговых решений, но не гарантируют прибыли. Перед открытием любой сделки необходимо тщательно проанализировать ситуацию на рынке, учитывая фундаментальные факторы и используя другие методы анализа. Управление рисками – неотъемлемая часть успешной торговли на Форексе. Никогда не рискуйте больше, чем можете себе позволить потерять. Используйте стоп-лоссы для ограничения потенциальных убытков.
Торговые стратегии с использованием индикаторов
Существует множество торговых стратегий, основанных на использовании индикаторов. Некоторые стратегии ориентированы на краткосрочную торговлю, другие – на долгосрочную. Выбор стратегии зависит от индивидуальных предпочтений и торгового стиля. Важно тщательно изучить выбранную стратегию и протестировать ее на демо-счете перед применением на реальном рынке.
Пример торговой стратегии с использованием MACD и RSI
Одна из простых стратегий предполагает использование MACD для определения тренда и RSI для определения перекупленности или перепроданности. Сигнал на покупку возникает, когда MACD пересекает нулевую линию снизу вверх, а RSI находится в зоне перепроданности. Сигнал на продажу возникает, когда MACD пересекает нулевую линию сверху вниз, а RSI находится в зоне перекупленности. Однако, перед открытием сделки необходимо подтвердить сигнал другими индикаторами или методами анализа.
- Шаг 1⁚ Анализ тренда с помощью MACD.
- Шаг 2⁚ Определение уровня перекупленности/перепроданности с помощью RSI.
- Шаг 3⁚ Подтверждение сигнала другими индикаторами.
- Шаг 4⁚ Установка стоп-лосса и тейк-профита.
- Шаг 5⁚ Открытие сделки.
Важно отметить, что данная стратегия является лишь примером, и ее эффективность может варьироваться в зависимости от рыночных условий. Необходимо постоянно адаптировать свою стратегию и учитывать изменения на рынке.
На странице https://example.com вы найдете дополнительную информацию о различных торговых стратегиях.
Обучение торговле на Форексе – это длительный и сложный процесс, требующий постоянного самосовершенствования и анализа. Успешные трейдеры постоянно изучают рынок, совершенствуют свои навыки и адаптируют свои стратегии к меняющимся условиям. Не стоит ожидать быстрой и легкой прибыли, будьте готовы к упорному труду и постоянному обучению. Использование индикаторов – лишь один из инструментов, который поможет вам на пути к успешной торговле на Форексе. Помните о важности управления рисками и никогда не инвестируйте средства, которые вы не можете позволить себе потерять. Грамотное использование индикаторов в сочетании с тщательным анализом рынка и дисциплинированным подходом к торговле – залог успеха на Форексе.
На странице https://example.com вы найдете еще больше полезной информации.
Описание⁚ Полное руководство по выбору и использованию индикатора для торговли на Форексе. Узнайте, как выбрать подходящий индикатор и использовать его для повышения эффективности вашей торговли.